Info: Version 1.8.x is available.
Last modified: $Date: 2024-03-30 11:25:00 +0000 (Sat, 30 Mar 2024) $
このページでは、 TOMOYO Linux の強制モードの使い方と、強制モードで動作中に発生したポリシー違反を処理する方法について説明します。
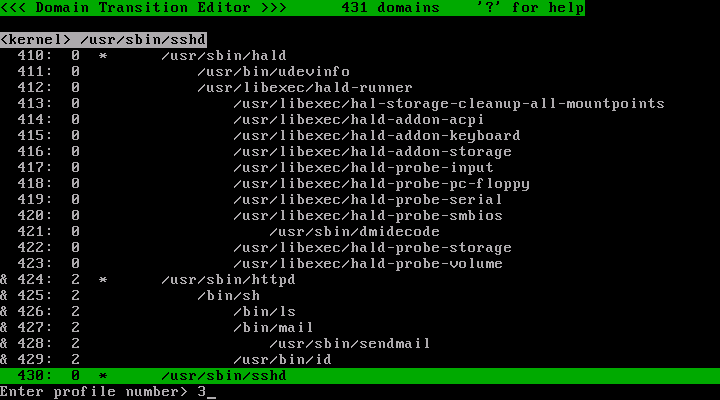
Apache に許可したい操作を全て行ったと判断したら、ポリシーエディタを実行してプロファイル番号を 3 に変更します。
ポリシーエディタを実行してください。対象となるドメインを選択し、 s キーを押して 3 と入力してから Enter キーを押します。

/usr/sbin/httpd およびその子孫のプロファイル番号が 3 に変化しました。
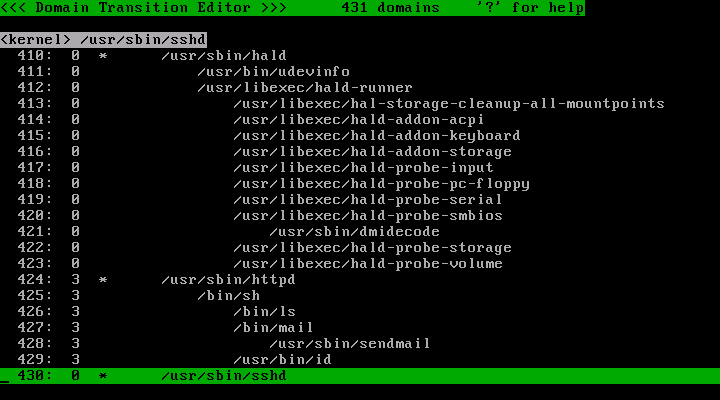
@ キーを押してプロセス一覧表示に切り替えてください。そして、 /usr/sbin/httpd プロセスとその子孫に対してプロファイル 3 が割り当てられていることを確認してください。
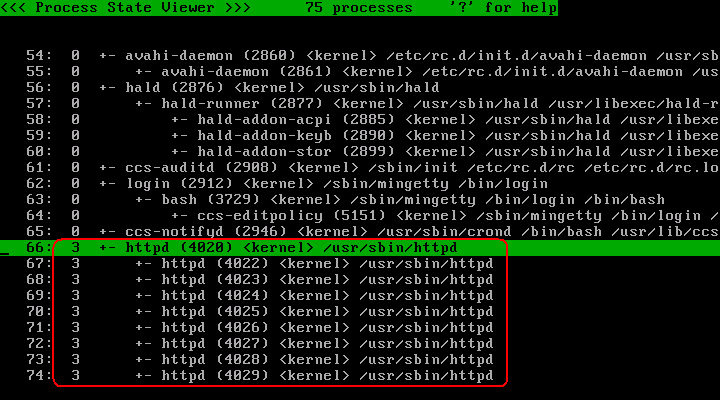
プロファイル 3 は強制モードを行うよう指定されているため、これにより /usr/sbin/httpd プロセスおよびその子孫は強制アクセス制御により保護された状態になりました。
q キーを押してポリシーエディタを終了してください。
ポリシーで許可されている操作をしてみましょう。
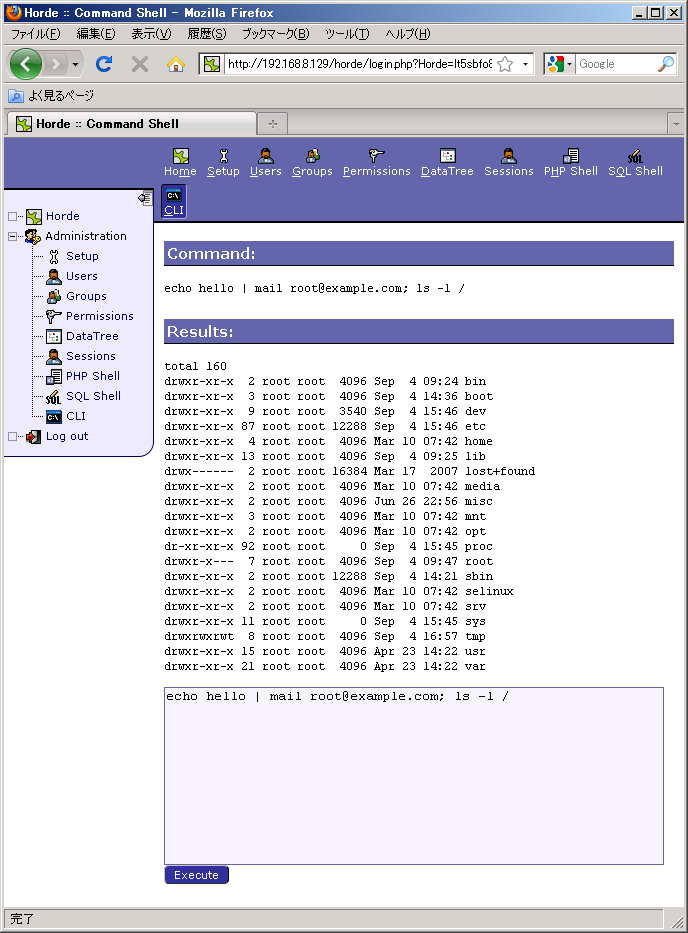
メールの送信はポリシーで許可されているので、操作は正常に終了しました。
ポリシーで許可されていない操作をしてみましょう。
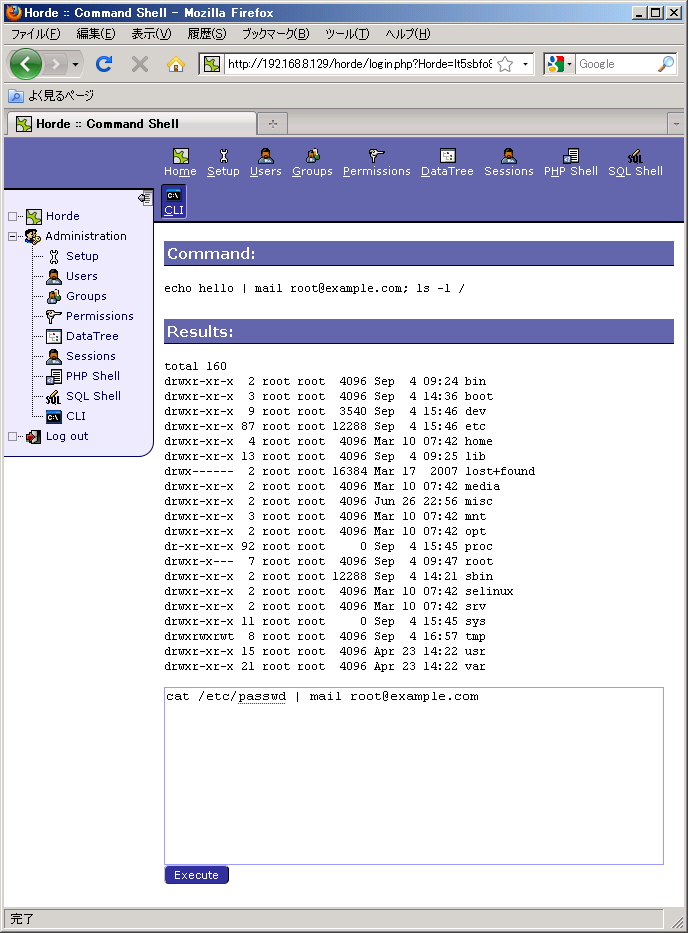
操作は拒否されました。(一見すると正常に終了したように見えますが、実際には /bin/mail が「入力が空っぽです」と警告しているとおり、 /bin/cat の実行が拒否されています。)
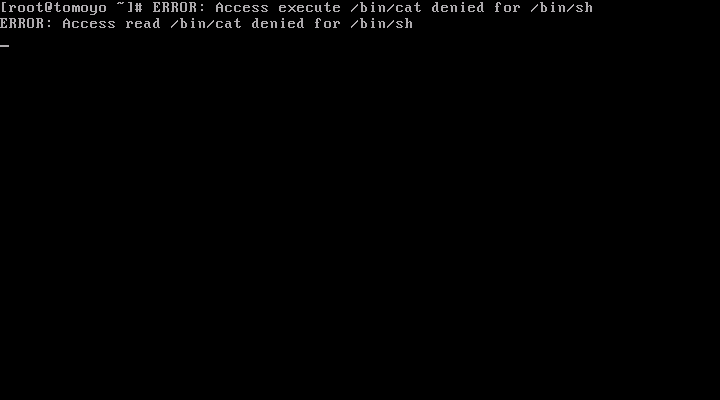
もしプロファイルで PREFERENCE::enforcing={ verbose=yes } と設定されている場合(デフォルトでそうなっています)、ポリシーで許可されていない操作を行うと ERROR: というメッセージがコンソールに表示されます。
もしアクセスログの設定を第2章: TOMOYO Linux の初期化で行っていた場合は、拒否されたアクセス要求を grep を使ってアクセスログから抽出することができます。
|
[root@tomoyo ~]# grep -A 3 -F 'profile=3 mode=enforcing' /var/log/tomoyo/reject_log.conf #2010-01-12 16:19:17# profile=3 mode=enforcing (global-pid=4836) task={ pid=4836 ppid=4835 uid=48 gid=48 euid=48 egid=48 suid=48 sgid=48 fsuid=48 fsgid=48 state[0]=0 state[1]=0 state[2]=0 type!=execute_handler } path1={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=917520 major=8 minor=1 perm=0755 type=file } path1.parent={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=917505 perm=0755 } exec={ realpath="/bin/cat" argc=2 envc=7 argv[]={ "cat" "/etc/passwd" } envp[]={ "TERM=linux" "PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin" "_=/bin/cat" "PWD=/usr/share/horde/admin" "LANG=en_US.UTF-8" "SHLVL=3" "LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8" } } <kernel> /usr/sbin/httpd /bin/sh allow_execute /bin/cat -- #2010-01-12 16:19:17# profile=3 mode=enforcing (global-pid=4836) task={ pid=4836 ppid=4835 uid=48 gid=48 euid=48 egid=48 suid=48 sgid=48 fsuid=48 fsgid=48 state[0]=0 state[1]=0 state[2]=0 type!=execute_handler } path1={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=917520 major=8 minor=1 perm=0755 type=file } path1.parent={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=917505 perm=0755 } <kernel> /usr/sbin/httpd /bin/sh allow_read /bin/cat |
最初のログは、 /usr/sbin/httpd から起動された /bin/sh から /bin/cat の実行が要求され、そのときの引数は cat /etc/passwd であったことを示しています。このログの1行目に mode=enforcing という内容が含まれているため、この要求は拒否されたことが判ります。
2番目のログは、 /usr/sbin/httpd から起動された /bin/sh が /bin/cat を読み込みモードでオープンしようとして拒否されたことを示しています。これは、要求されたプログラムを実行できなかった場合そのプログラムの内容を確認するために読み込みモードでオープンしようとするという習性が /bin/sh にあるためです。
もし通知設定を第2章: TOMOYO Linux の初期化で行っていた場合は、 ccs-notifyd から送られたメールが届くはずです。このメールの内容は、ヘッダにシリアルナンバーが付与されている点を除いてアクセスログと同一内容です。
|
[root@tomoyo ~]# mail Mail version 8.1 6/6/93. Type ? for help. "/var/spool/mail/root": 1 message 1 unread >U 1 root@localhost.local Tue Jan 12 16:19 18/1234 & Message 1: From root@localhost.localdomain Tue Jan 12 16:19:17 2010 Date: Tue, 12 Jan 2010 16:19:17 +0900 From: root <root@localhost.localdomain> To: root@localhost.localdomain Q0-0 #2010-01-12 16:19:17# profile=3 mode=enforcing (global-pid=4836) task={ pid=4836 ppid=4835 uid=48 gid=48 euid=48 egid=48 suid=48 sgid=48 fsuid=48 fsgid=48 state[0]=0 state[1]=0 state[2]=0 type!=execute_handler } path1={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=917520 major=8 minor=1 perm=0755 type=file } path1.parent={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=917505 perm=0755 } exec={ realpath="/bin/cat" argc=2 envc=7 argv[]={ "cat" "/etc/passwd" } envp[]={ "TERM=linux" "PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin" "_=/bin/cat" "PWD=/usr/share/horde/admin" "LANG=en_US.UTF-8" "SHLVL=3" "LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8" } } <kernel> /usr/sbin/httpd /bin/sh allow_execute /bin/cat |
プロファイルで PREFERENCE::enforcing={ penalty=1 } と設定することで、強制モードでポリシー違反が発生した場合に、ポリシー違反の原因となったプロセスを 0.1 秒間スリープ状態にさせることができます。無限ループの中でポリシー違反が発生した場合に、CPU使用率が 100% になってしまうのを回避するのに役にたちます。ハイジャックされた Samba サーバプロセスがポリシーで許可されていない要求を繰り返すことによりCPUを浪費している状況について以下のムービーで紹介しています。
システムの振る舞いをポリシーにより制限しているため、パッケージのアップデートに伴いポリシーの更新が必要になる場合があります。
以下のいずれかの場合に、ポリシーの更新が必要になります。
学習モードを使ってポリシーを最初から再取得するのが理想です。しかし、現実には、一度強制モードでの運用を開始したシステムを強制モード以外に変更することは困難です。ドメイン単位で強制モードにするかどうかを指定できますが、強制モードではないドメインに属しているアプリケーションの制御を奪われたら意味がありません。例えば、 http サーバのアクセス許可を再取得するために http サーバだけを学習モードにするだけでも、システム全体が無防備になってしまうわけです。そのため、 TOMOYO Linux では、強制モードのまま、パッケージのアップデートとポリシーの修正を行います。
TOMOYO Linux には、強制モードのままポリシーの修正を行うためのツールが付属しています。これらのツールを使うことで、軽微な変更ならば、ポリシーを最初から再取得することなくシステムの運用を継続できます。ただし、これらのツールは、全てのケースに対応できるとは限らず、最適なポリシーであることを保証するものではありません。
実際の操作手順について以下のムービーで紹介しています。
|
[root@tomoyo ~]# /usr/sbin/ccs-queryd Monitoring /proc/ccs/query and /etc/ld.so.cache . Press Ctrl-C to terminate. #2010-01-10 12:27:10# profile=3 mode=enforcing (global-pid=4210) task={ pid=4210 ppid=4205 uid=0 gid=0 euid=0 egid=0 suid=0 sgid=0 fsuid=0 fsgid=0 state[0]=0 state[1]=0 state[2]=0 type!=execute_handler } path1={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=1766 major=0 minor=17 perm=0666 type=char dev_major=1 dev_minor=3 } path1.parent={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=962 perm=0755 } <kernel> /etc/rc.d/init.d/sshd allow_ioctl /dev/null 0x5401 Allow? ('Y'es/'N'o/'R'etry/'S'how policy/'A'dd to policy and retry):s # select global-pid=4210 <kernel> /etc/rc.d/init.d/sshd use_profile 3 allow_read /bin/bash allow_read/write /dev/tty allow_capability SYS_IOCTL allow_read/write /dev/pts/\$ allow_read /usr/lib/locale/locale-archive allow_read /etc/nsswitch.conf allow_read /etc/passwd allow_read /etc/rc.d/init.d/sshd allow_read /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions allow_execute /sbin/consoletype if exec.realpath="/sbin/consoletype" exec.argv[0]="/sbin/consoletype" allow_read /etc/profile.d/lang.sh allow_read /etc/sysconfig/i18n allow_read /etc/sysconfig/init allow_execute /sbin/runlevel if exec.realpath="/sbin/runlevel" exec.argv[0]="runlevel" allow_execute /bin/cp if exec.realpath="/bin/cp" exec.argv[0]="cp" allow_execute /usr/sbin/sshd if exec.realpath="/usr/sbin/sshd" exec.argv[0]="/usr/sbin/sshd" allow_execute /bin/touch if exec.realpath="/bin/touch" exec.argv[0]="touch" allow_read/write /dev/console allow_execute /bin/unicode_start if exec.realpath="/bin/unicode_start" exec.argv[0]="/bin/unicode_start" allow_read /var/run/sshd.pid allow_write /dev/null allow_capability SYS_KILL allow_signal 15 <kernel> /usr/sbin/sshd allow_execute /bin/usleep if exec.realpath="/bin/usleep" exec.argv[0]="usleep" allow_execute /bin/rm if exec.realpath="/bin/rm" exec.argv[0]="rm" allow_execute /usr/bin/killall if exec.realpath="/usr/bin/killall" exec.argv[0]="killall" allow_execute /usr/bin/rhgb-client if exec.realpath="/usr/bin/rhgb-client" exec.argv[0]="/usr/bin/rhgb-client" allow_execute /bin/sleep if exec.realpath="/bin/sleep" exec.argv[0]="sleep" allow_signal 1 <kernel> /usr/sbin/sshd allow_ioctl /dev/console 0x5401 allow_ioctl /etc/rc.d/init.d/sshd 0x5401 allow_ioctl /var/run/sshd.pid 0x5401 allow_ioctl /dev/pts/\$ 0x5401 #2010-01-10 12:27:20# profile=3 mode=enforcing (global-pid=4210) task={ pid=4210 ppid=4205 uid=0 gid=0 euid=0 egid=0 suid=0 sgid=0 fsuid=0 fsgid=0 state[0]=0 state[1]=0 state[2]=0 type!=execute_handler } path1={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=1766 major=0 minor=17 perm=0666 type=char dev_major=1 dev_minor=3 } path1.parent={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=962 perm=0755 } <kernel> /etc/rc.d/init.d/sshd allow_ioctl /dev/null 0x5401 Allow? ('Y'es/'N'o/'R'etry/'S'how policy/'A'dd to policy and retry):a Enter new entry> allow_ioctl /dev/null 0x5401 Added 'allow_ioctl /dev/null 0x5401'. The pathname /usr/lib/libpurple.so.0.6.3 was created. Appended to globally readable file. The pathname /usr/lib/libpurple-client.so.0.6.3 was created. Appended to globally readable file. ---------------------------------------- #2010-01-10 12:29:35# profile=3 mode=enforcing (global-pid=4561) task={ pid=4561 ppid=4557 uid=0 gid=0 euid=0 egid=0 suid=0 sgid=0 fsuid=0 fsgid=0 state[0]=0 state[1]=0 state[2]=0 type!=execute_handler } path1={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=1507379 major=8 minor=1 perm=0755 type=file } path1.parent={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=1507329 perm=0755 } exec={ realpath="/bin/sleep" argc=2 envc=6 argv[]={ "sleep" "1" } envp[]={ "TERM=xterm" "PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin" "PWD=/" "LANG=en_US.UTF-8" "SHLVL=1" "_=/bin/sleep" } } <kernel> /etc/rc.d/init.d/cups allow_execute /bin/sleep Allow? ('Y'es/'N'o/'R'etry/'S'how policy/'A'dd to policy and retry):a Enter new entry> allow_execute /bin/sleep if exec.argc=2 exec.argv[1]="1" Added 'allow_execute /bin/sleep if exec.argc=2 exec.argv[1]="1"'. #2010-01-10 12:29:55# profile=3 mode=enforcing (global-pid=4561) task={ pid=4561 ppid=4557 uid=0 gid=0 euid=0 egid=0 suid=0 sgid=0 fsuid=0 fsgid=0 state[0]=0 state[1]=0 state[2]=0 type!=execute_handler } path1={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=1507379 major=8 minor=1 perm=0755 type=file } path1.parent={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=1507329 perm=0755 } exec={ realpath="/bin/sleep" argc=2 envc=6 argv[]={ "sleep" "1" } envp[]={ "TERM=xterm" "PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin" "PWD=/" "LANG=en_US.UTF-8" "SHLVL=1" "_=/bin/sleep" } } <kernel> /etc/rc.d/init.d/cups # wants to create domain <kernel> /etc/rc.d/init.d/cups /bin/sleep Allow? ('Y'es/'N'o/'R'etry):y #2010-01-10 12:29:58# profile=3 mode=enforcing (global-pid=4561) task={ pid=4561 ppid=4557 uid=0 gid=0 euid=0 egid=0 suid=0 sgid=0 fsuid=0 fsgid=0 state[0]=0 state[1]=0 state[2]=0 type!=execute_handler } path1={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=707247 major=8 minor=1 perm=0644 type=file } path1.parent={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=688142 perm=0755 } <kernel> /etc/rc.d/init.d/cups /bin/sleep allow_read /usr/lib/locale/locale-archive Allow? ('Y'es/'N'o/'R'etry/'S'how policy/'A'dd to policy and retry):a Enter new entry> allow_read /usr/lib/locale/locale-archive Added 'allow_read /usr/lib/locale/locale-archive'. ---------------------------------------- #2010-01-10 12:30:10# profile=3 mode=enforcing (global-pid=4630) task={ pid=4630 ppid=4629 uid=0 gid=0 euid=0 egid=0 suid=0 sgid=0 fsuid=0 fsgid=0 state[0]=0 state[1]=0 state[2]=0 type!=execute_handler } path1={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=955698 major=8 minor=1 perm=0666 type=socket } path1.parent={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=950312 perm=0755 } <kernel> /usr/sbin/acpid allow_unlink /var/run/acpid.socket Allow? ('Y'es/'N'o/'R'etry/'S'how policy/'A'dd to policy and retry):a Enter new entry> allow_unlink /var/run/acpid.socket if path1.type=socket Added 'allow_unlink /var/run/acpid.socket if path1.type=socket'. The pathname /usr/lib/libpurple.so.0.5.9 was deleted. Deleted from globally readable file. The pathname /usr/lib/libpurple-client.so.0.5.9 was deleted. Deleted from globally readable file. |
ccs-queryd は、 /etc/ld.so.cache に登録されている共有ライブラリファイルの情報が変更された場合に、共有ライブラリのパス名を「無条件に読み込み可能なファイル」として例外ポリシーに追加します。例えば、
| The pathname /usr/lib/libpurple.so.0.6.3 was created. Appended to globally readable file. |
というメッセージは /usr/lib/libpurple.so.0.6.3 というパス名が作成されて /etc/ld.so.cache に登録されたので例外ポリシーに追加したことを示しています。
また、「無条件に読み込み可能なファイル」として例外ポリシーに登録されているパス名が消滅した場合、例外ポリシーから削除します。例えば、
| The pathname /usr/lib/libpurple.so.0.5.9 was deleted. Deleted from globally readable file. |
というメッセージは /usr/lib/libpurple.so.0.5.9 というパス名が消滅したのでポリシーから削除したことを示しています。
パッケージをアップデート中に、デーモンの再起動などでポリシー違反が発生するかもしれません。ポリシー違反が発生した場合、 ccs-queryd にプロンプトが表示されます。
|
#2010-01-10 12:29:35# profile=3 mode=enforcing (global-pid=4561) task={ pid=4561 ppid=4557 uid=0 gid=0 euid=0 egid=0 suid=0 sgid=0 fsuid=0 fsgid=0 state[0]=0 state[1]=0 state[2]=0 type!=execute_handler } path1={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=1507379 major=8 minor=1 perm=0755 type=file } path1.parent={ uid=0 gid=0 ino=1507329 perm=0755 } exec={ realpath="/bin/sleep" argc=2 envc=6 argv[]={ "sleep" "1" } envp[]={ "TERM=xterm" "PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin" "PWD=/" "LANG=en_US.UTF-8" "SHLVL=1" "_=/bin/sleep" } } <kernel> /etc/rc.d/init.d/cups allow_execute /bin/sleep Allow? ('Y'es/'N'o/'R'etry/'S'how policy/'A'dd to policy and retry): |
上記の例は、 <kernel> /etc/rc.d/init.d/cups というドメインに属しているプロセスが sleep 1 というコマンドラインを処理するために /bin/sleep の実行を要求したが、ポリシーによって拒否されたので、あなたの判断を仰いでいることを示しています。 アクセス要求の妥当性を判断して、答えを指定してください。 Y を押すと許可、 N を押すと拒否、 R を押すと再試行されます。また、 S を押すとそのプロセスのドメイン用ポリシが表示されます。 A を押すと編集した上でドメイン用ポリシーに追加後、再試行できます。
無条件にアクセス要求を許可しないようにしてください。ポリシー違反の原因がパッケージのアップデートによるものとは限らず、侵入者の攻撃によるものである可能性があるからです。もし、侵入者の攻撃によって発生したアクセス要求に対してアクセスを許可してしまった場合、侵入されてしまいます。
ccs-queryd が動作している場合、ポリシーによって拒否されたアクセス要求は、あなたが応答するまで保留状態となります。そのため、 ccs-queryd を動作させたままログアウトしないでください。
次に、強制アクセス制御の対象となっているプログラムの動作を確認するために、一通りの操作を試してください。もし、アクセス許可の不足が検出された場合は ccs-queryd に表示されますので、 ccs-queryd の監視を忘れないようにしてください。
なお、 ccs-queryd はメモリ上のポリシーを直接編集します。シャットダウンすると失われてしまいますので、忘れずに ccs-savepolicy を実行してポリシーを保存してください。
| [root@tomoyo ~]# /usr/sbin/ccs-savepolicy |
以上でパッケージの更新作業は完了です。 ccs-queryd を実行していたコンソールまたはターミナルを閉じてください。